Almost everyone is aware of the OS running on Apple Computers. Its called OS X & each version gets a name from a location in California (they used cat names earlier). But what is little know is about the Server that is also made available from Apple. Its called as OS X Server. Not only is it little know but it is also under utilised. I am going to make a case for using this product as compared to some of the other solutions that are available out there.
Installing
Firstly, lets talk about getting hold os OS X Server. Earlier there used to be a dedicated version of the OS which was made available for the server. But starting OS X 10.7 (Lion) that approach was discontinued. If you wanted an OS X Server, you would have to first upgrade your Mac to the consumer version of the OS & then install the Server.app. All you have to do This greatly simplified the whole process of setting your Mac up as a server.
The big advantage with this is that you no longer need to purchase a separate “server” version of the OS. The other big advantage is that all the services being offered by the server are no located in a single application, in a nice collected manner.
Requirements
Typically most servers require an advanced hardware configuration to run. This is also the case for OS X Server. The recommended products for this would be the Mac Pro or the Mac Mini Server. The Mac Mini Server is a Mac Mini that comes with the Server App included as a part of the setup. This is a product configured to be used as a server. While the 2 products mentioned above are ones used most frequently as a server, you are not limited to them. Any Mac with a minimum of 10GB storage space & 2GB of RAM can run OS X Server. Though in reality you would need much larger specs than the ones mentioned above.
Services Offered
The OS X Server works best in an all Apple product environment. However, it also works well in mixed environments too. Especially when it comes to managing Macs & iOS Devices while taking advantage of other services being offered. In fact, a solution commonly used is the “Magic Triangle” which allows you to used an Active Directory Server along with OS X Server.
Basic Networking Services
Basics Networking Services such as DNS, DHCP, VPN are easily available & configured. Most of them don’t require a lot of configuring to do. Also the Caching Service & Software Update services can also be easily configured for managing the bandwidth usage in the organisation.
Collaboration & Communication
As a part of the collaboration & communication services provided you have the ability to host your own Mail service, Messages service, Website service, Wiki service, Calendar & Contacts Service.
Sharing
The file sharing service & ftp services are available for users to more easily share files & folders across the network.
Management
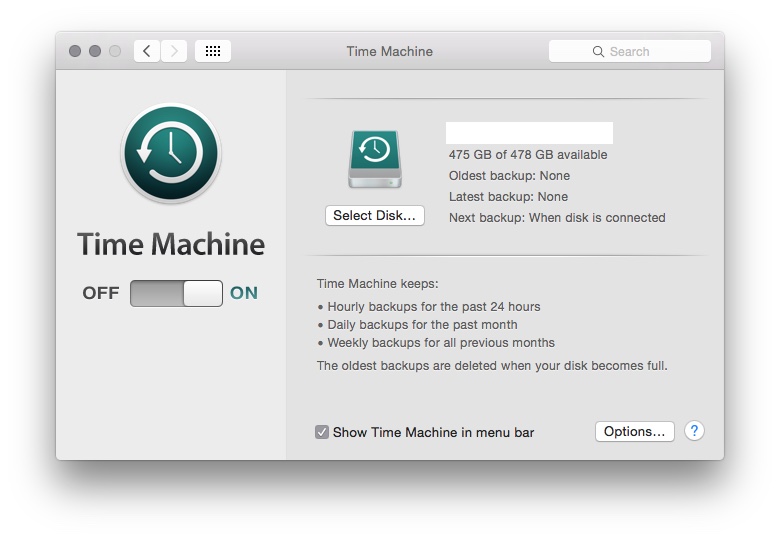
From a device management point of view there are plenty of services available. You have the Netinstall service which allows you to remote install OS X over the network or allow clients to boot using an image which is hosted on the server. Then there is the Open Directory Service which allows the management of various user accounts over the network. These users accounts then work along with the Time Machine service, which allows you to back up a Mac onto the server itself. Finally, the Profile Manager service works along with the domain users to provide device management for the different devices (OS X & iOS Devices).
Tools
Server App
LINK:https://itunes.apple.com/in/app/os-x-server/id714547929?mt=12
This is the main app that you will use to configure the different services that your server will be offering. The advantage with the app is it also allows you to remotely administer your server using the app itself.
Workgroup Manager
LINK:http://support.apple.com/kb/dl1698
The Workgroup Manager is a utility which can be downloaded from Apple’s support page. This application was used to create users & groups & apply managed preferences to them for earlier versions of the server. It is possible to create users & groups for the current version of the server using this app.
System Image Utility
This tool is required to create the different types of NetInstall images which are used for mass deployment. All OS X computers come with this application preinstalled.
Directory Utility
This utility also comes built into the OS & is used while binding your Mac to a Directory Service.
Apple Remote Desktop
LINK:https://itunes.apple.com/in/app/apple-remote-desktop/id409907375?mt=12
This is a very powerful tool. Available on the Mac App Store as a paid app. This tool allows you to remotely monitor & administer all the Macs within your organisation. It has many report generation tools to help in the management of your Macs.
Apple Configurator
LINK:https://itunes.apple.com/in/app/apple-configurator/id434433123?mt=12
This is another application available on the app store. This is a free app to configure different iOS Devices. It is used to perform a manual configuration of the devices.
Ticket Viewer
The Ticket Viewer Application is a built in application that is used to help in examining tickets used under kerberos.
Recovery Disk Assistant
LINK:http://support.apple.com/kb/dl1433
A free tool that is available online which allows an administrator to create an external bootable recovery drive to perform various troubleshooting tasks. OS X: About Recovery Disk Assistant
Disk Utility
This is a built in utility that is used to maintain different storage devices. It allows you to partition & format various drives.
Why to use the OS X Server
There are many reasons why an OS X Server would make a good option.
- Cost: The cost of OS X Server itself is low. The hardware for running OS X Server would ideally be the Mac Mini which starts around $999 (including the Server App itself). If you already have a Mac with you, you just need to purchase the Server App for $20. This is ideal for organisations on a budget.
- Simplicity: The Server is very easy to configure. Many of the services being provided are extremely easy to configure & maintain. From an administrators point of view, it involves providing basic information & a few clicks.
- Features: The Server provides many basic services used everyday & many administrative options that combine the power of modern day servers with the simplicity needed.
- Works well along with other Servers such Windows Server.
Ideal Situations to use OS X Server
The OS X Server is ideal for small organisations which use Mac or iOS Devices. The low cost & simplicity makes it an ideal choice for such organisations. Also if you are an organisation which uses a lot of Macs & iOS Devices then managing them is a lot easier with OS X Server, here again the cost & simplicity ensures that it is a viable option.
The server may not be a good choice for organisations with a very large user base or very few Mac/iOS devices. While other computers can easily work with OS X Server, other Servers may prove much better for such scenarios.
Here are some points to consider while deciding whether to use an OS X Server.
- Does your organisation use a lot of Macs &/or iOS Devices?
- Do you need to perform various administrative & configuration tasks on your Apple devices?
- Is your user base small? Approximately 10 – 150 odd employees?
- Do you need to provide very basic services without worrying too much about platforms being used? (Especially if directory services are not required).
If the answer to a combination of questions above is Yes, then the OS X Server might be the right choice for you.
Below are a list of some scenarios where the OS X Server might be ideal
- Small Medium Enterprises
- Schools & Educational Institutions
- All Mac & iOS Environments
- Home
Conclusion
The OS X Server is best if you are predominantly using Apple computers & mobile devices. The ability to manage them & configure them is best served by the Server app. However, for larger organisations this may not be the only criteria. The server can work along with windows server, however, most Apple computers & mobile devices can also work with other solutions.
If cost is a major consideration & simplicity is a must then the OS X Server is a good bet. If you are looking for a feature heavy server which offers a wide variety of services with lots of room for customisation then this might not be the right solution.
All in all the Server App is a very good app. It will definitely be something work considering when you are managing the IT infrastructure.




 There are other third party tools which you could use if you wish.
There are other third party tools which you could use if you wish.