This is the third part in the 3 part series on Apple ID & iCloud. This part touches on enterprise specific aspects.
Here are the links to Part 1 & Part 2.
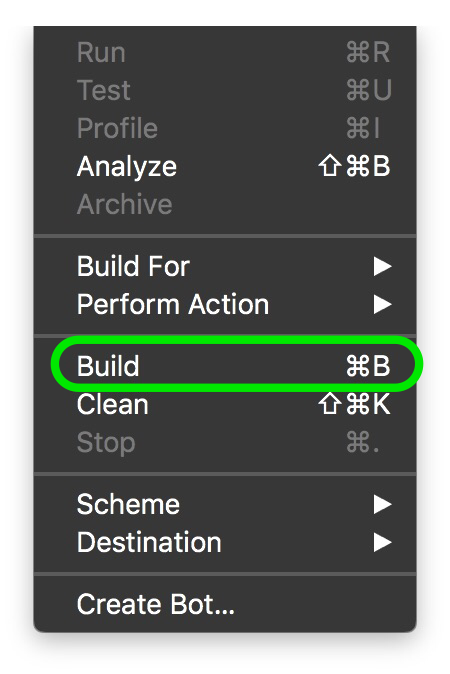
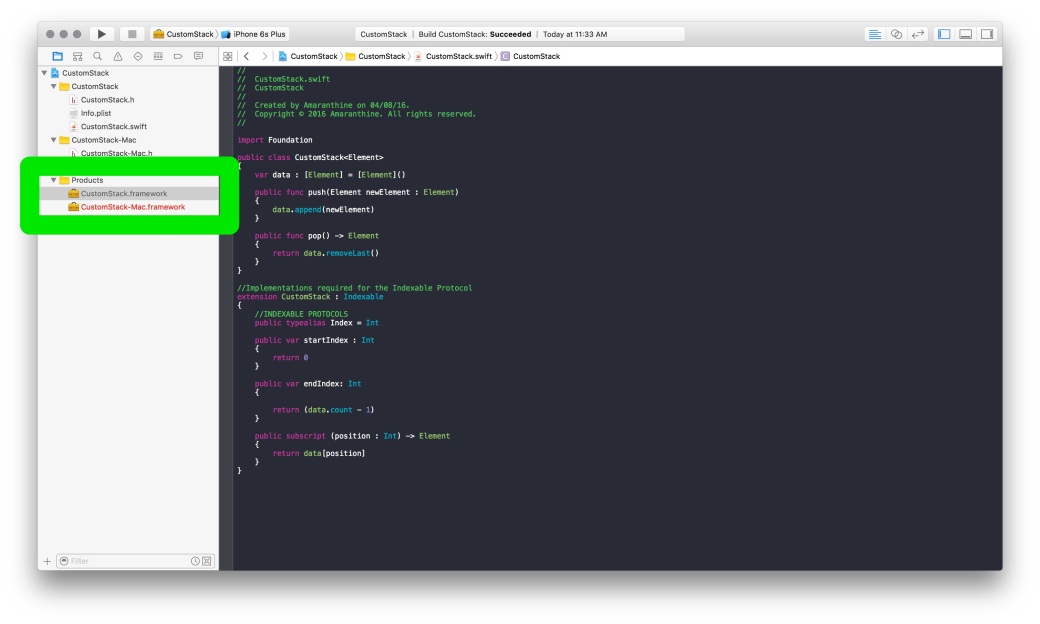
Creating Swift Frameworks is easy. The steps below walk you through creating a Swift Framework. The steps below have been performed on Xcode 7.3
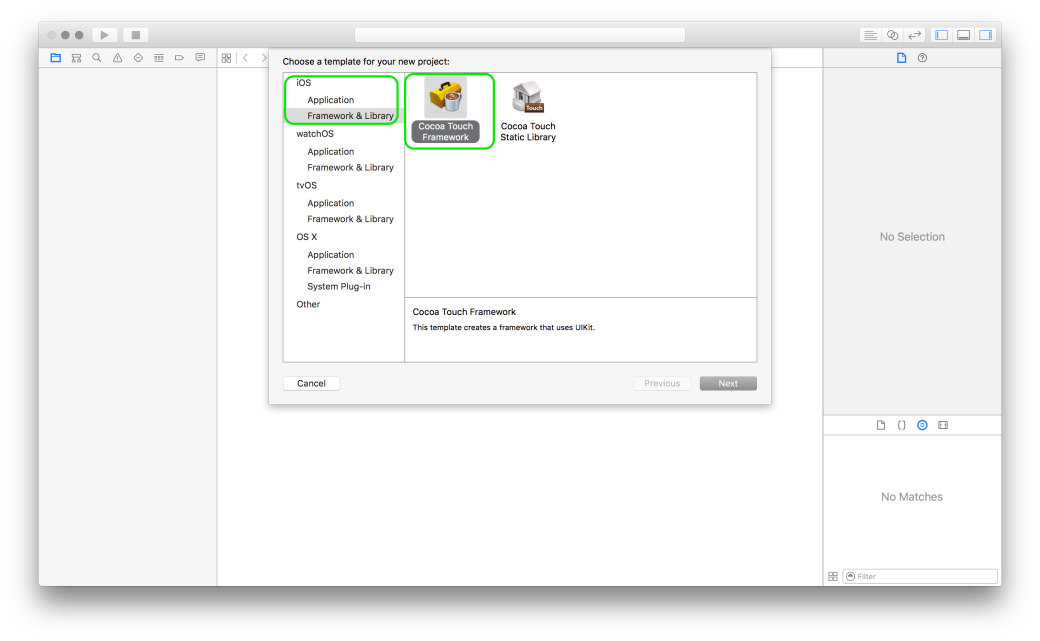
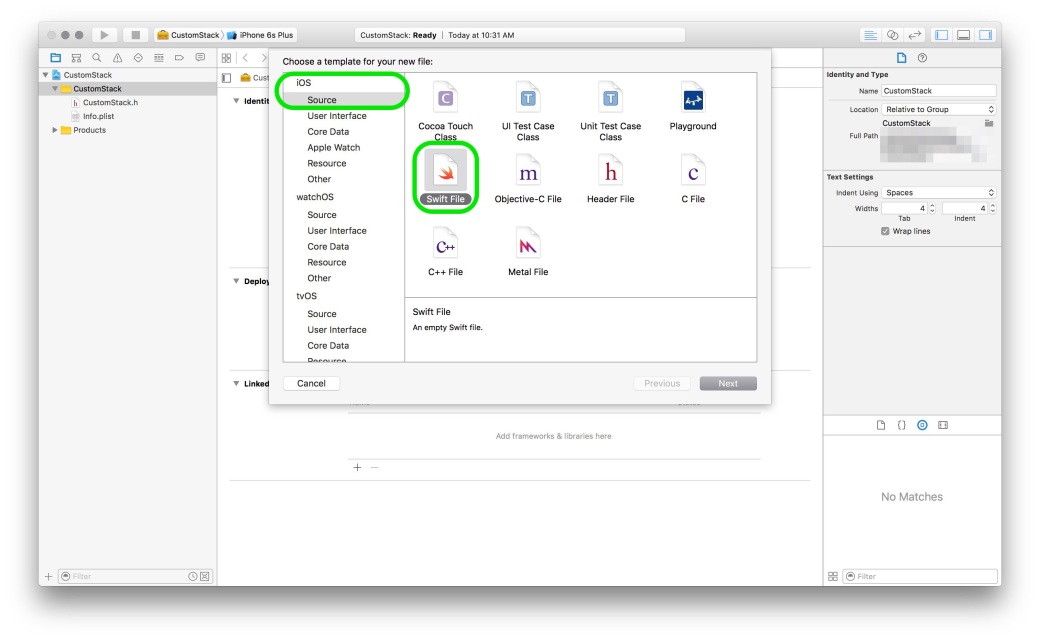
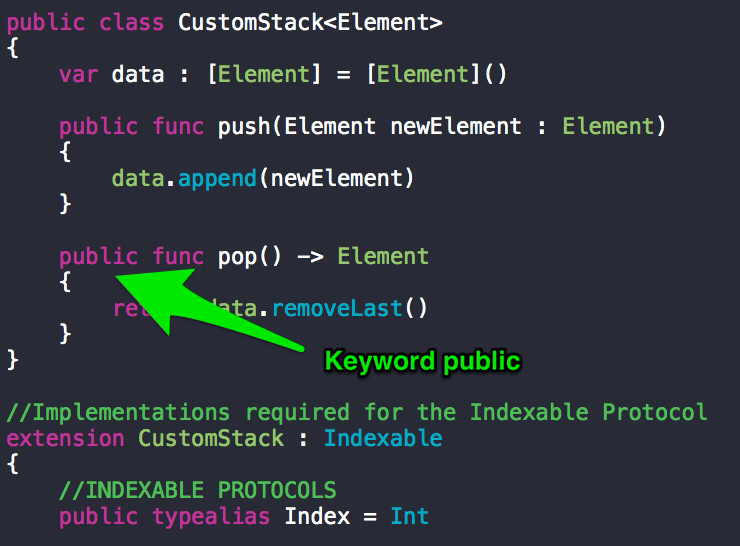
Different variables/classes/functions that are declared within a module are accessible freely within the module. Swift files contain code & are themselves found within Swift modules. So a module can mean project or a framework.So, to access the variables/functions/classes from module A in module B, we have to make those elements of module A public in order to access them in module B.
For more information, do read Apple’s Swift Documentation.
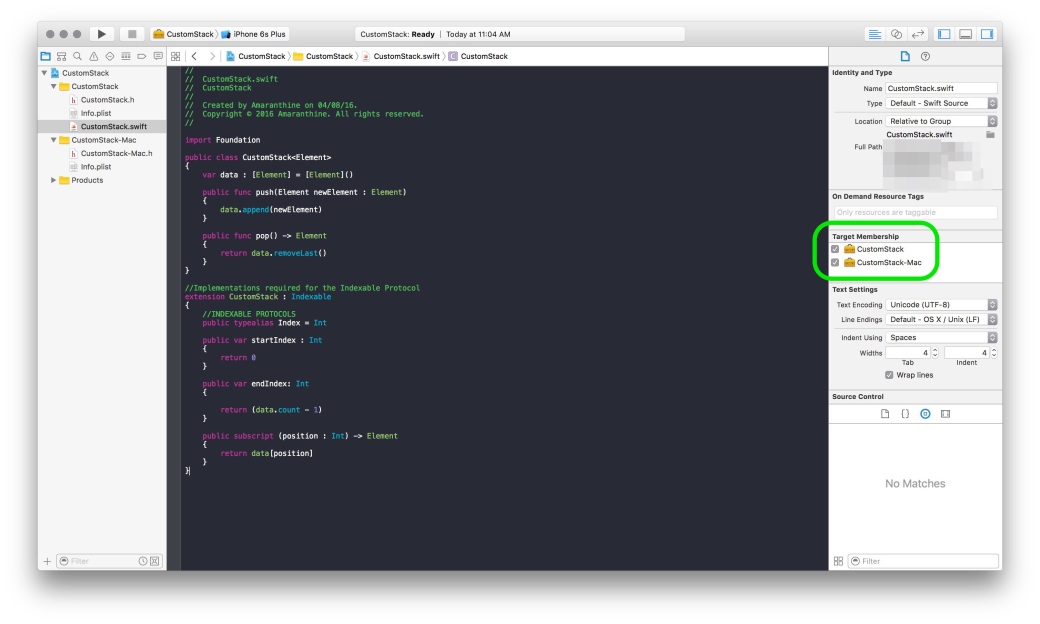
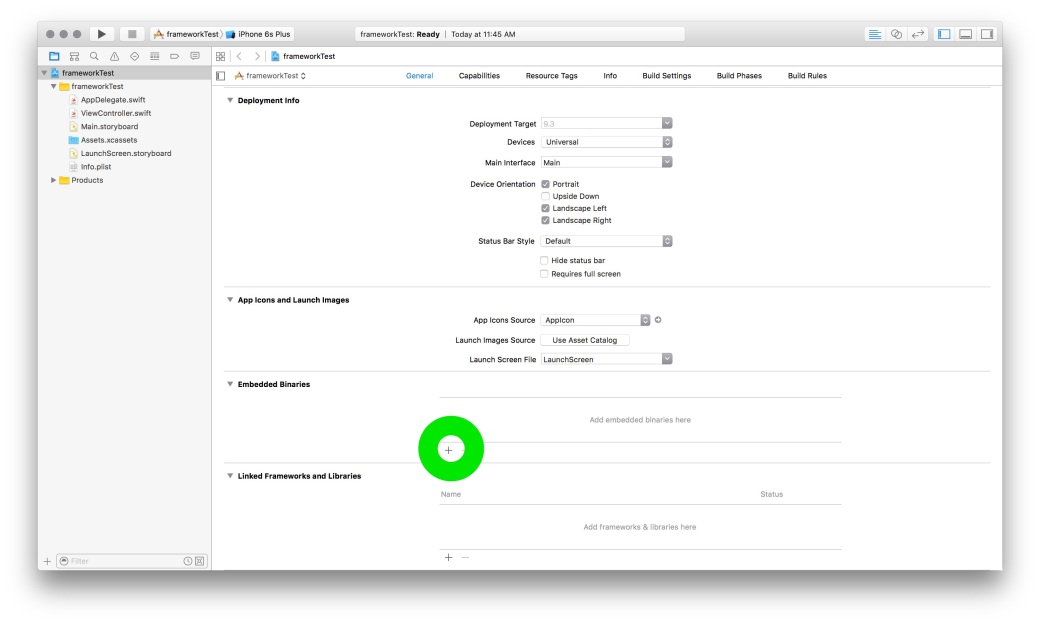
The process of creating a mixed library is straightforward. Its almost the same as above with some minor differences.
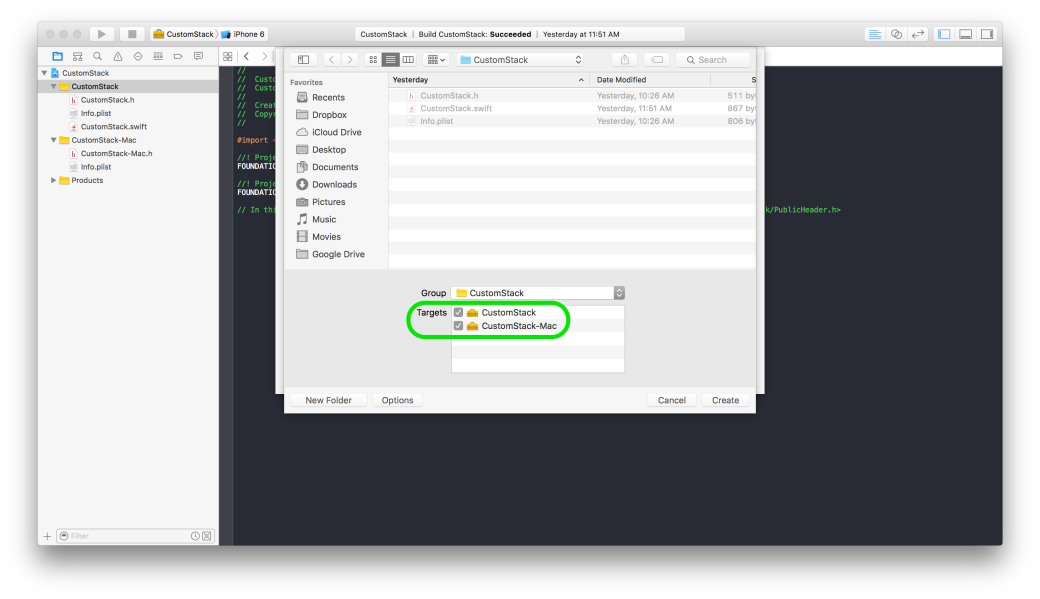
#import "<FrameworkName>/<HeaderName>.h
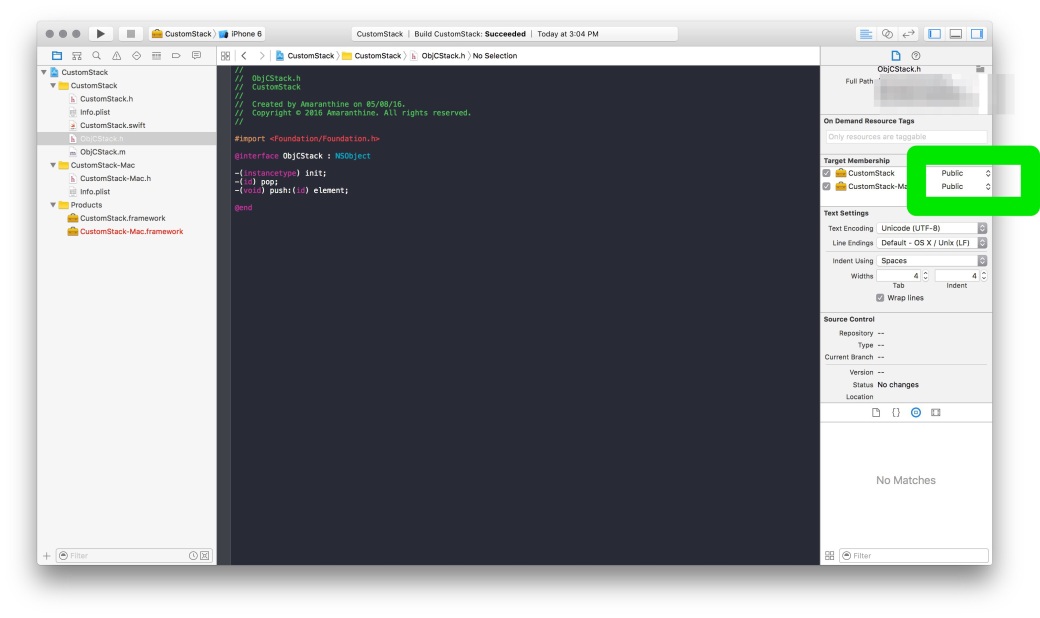
#import "<FrameworkName>/<FrameworkName>-Swift.h"
Replace the word FrameworkName with the name of your Framework.
Apple’s devices are getting more and more popular by the day. People are really excited to get hold of the newest product that comes out of its stable. This guide walks you through some of the things you need to keep in mind while buying used devices or selling your existing device. This may not apply when buying a new product from the store for the first time, however, its still good to know these things & run your device through a checklist.
Note the checklist provided below is by no means comprehensive nor is it complete. There might be other things to keep in mind before buying &/or selling used devices, depending on the geographic area, situation, and circumstances.
Before buying a used products run them through this checklist. Some items are device specific.
The list above should give you a good idea on what you need to do while planning to sell your Apple device.


Enterprises may take additional steps
These are some of the things that you can do to make the transaction easy on both the sides.
For best viewing please make sure the quality is set to 720p 60 HD.
 Swift Programming on Linux
Swift Programming on LinuxThe steps below walk you through the process of downloading, installing & using the Swift Programming language on Linux. For this I will be using Ubuntu Linux 14.04.3 LTS version.
The following are some commands that you can use for Configuration &/or Troubleshooting. This list is by no means exhaustive. Do check the man pages for more information. This article assumes familiarity with Terminal commands. If you are new to the Terminal Application, please read the following articles before reading this one.
Terminal Commands for OS X – Basic
Terminal Commands for OS X – Part 2
Terminal Commands for OS X – Part 3
softwareupdate
This command is used to install software updates remotely. View the following support article for more information.
dscl
This command is used to manage the different Users & Groups on your Mac. Using this command one can create, modify & view the different settings related to Users & Groups locally on the Mac. Amongst the other things, User Authentication through passwords can also be managed from here. View the man page for more information on the options available.
createhomedir
This command is used to create & populate home folders on the Mac. View the man page for more information on the options available.
systemsetup
As the name says, this command is used to setup the system. One of the more generic commands, using this we can set the date/time, energy preferences & various other settings. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
security
This is the command line version of the GUI application Keychain Access. Use this command to manage your Keychain. Some of the things that can be done using this command include: creating keychains, locking/unlocking keychains, finding your secure information within the Keychain. View the man page for more information on the options available.
fsck
This command is used for running File System Checks. View the man page for more information on the options available.
diskutil
This command is used to run disk utility options. This is the command line equivalent of the Disk Utility application. There are many operations available within this command line utility that are not available directly in the GUI version of the tool. View the man page for more information on the options available.
fdesetup
This command is used to control the FileVault settings on the Mac. Again, like the distil command this utility gives a lot more options than the GUI version of the Mac. Including the ability to change the recovery keys. View the man page for more information on the options available.
chmod
This command is used to modify permissions to files & folders. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
ln
This is the command used to create both hard links & soft links in the terminal. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
xattr
This command is used to examine &/or modify the attributes/metadata for a given file or folder. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
tmutil
This command allows you to configure &/or setup the Time Machine service. This is the command line version of the Time Machine settings located within System Preferences. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
locate
This command is used to search for files on the Mac. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
hdiutil
This command is also used to manage storage devices & Filesystems. The diskutil & hdiutil are command line versions of the Disk Utility app. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
networksetup
This command is used to set up & configure your network settings. This is the command line equivalent of the Network Preferences located under System Preferences. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
ipconfig
This command lets you view & control the IP configuration settings. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
ifconfig
This command is used to configure the Network Interface parameters. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
route
This command allows you to manually manipulate the routing tables. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
ping
Used to send ping diagnostic requests. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
scutil
Used to manage the System Configuration parameters. View the man page for more information on the different options available.
shutdown
This command is used to shut down the Mac from the command line. View the man page for more information on the options available.
sleep
This command is used to put the system to sleep. View the man page for more information on the options available.
reboot/halt
This command is used for restarting the system. View the man page for more information on the options available.
caffeinate
Used to prevent the system from sleeping. View the man page for more information on the options available.
There are various editors available for command line. I am just listing a few. A lot of the editing can also be done in the GUI but in some cases the changes have to be done as a Super User. In Such situations loading one of the following editors using the sudo command can come in handy.
Emacs
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emacs
https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/
http://www.xemacs.org
Vi
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vi
Vim
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vim_(text_editor)
http://www.vim.org
GEdit
This article covers some of the things troubleshooters would need during their everyday work. I’ve also listed links to some products and applications as an example. It is by no means an endorsement of the same.
OS X Install Disk: This is probably one of the most important tool that a troubleshooter must carry around with him/her. Ideally it would be one disk with multiple versions, each corresponding to a specific version of the OS. Exactly how many versions depends on the situation, for example one can have all instances of the present and previous 2 versions of the OS (For example OS X Mavericks 10.9, 10.9.1, 10.9.2, 10.9.3, 10.9.4, 10.9.5 OS X Yosemite 10.10, 10.10.1, 10.10.2, 10.10.3, 10.10.4, 10.10.5 OS X El Capitan 10.11, 10.11.1)
Thunderbolt & FireWire Cables: These come in handy when it comes to transferring data. These cables are necessary when you wish to perform target disk mode troubleshooting. Make sure you have the correct version of the cable.
http://www.apple.com/shop/product/MD862LL/A/apple-thunderbolt-cable-05-m
Portable Storage Device: Along with the cables mentioned earlier having a portable storage device with a large capacity is useful. Mainly when it comes to taking a back up. The user may or may not have a storage device available for this. (Ideally, taking a backup of the data should be done by the user on his/her own storage device.)
http://www.lacie.com/as/en/products/mobile-storage/rugged-thunderbolt/
http://www.promise.com/Products/Pegasus
Internet access via USB Dongle: Yet another important tool. Application & OS upgrades require internet access. This will also come in handy when you are trying to perform network troubleshooting. Make sure there is sufficient data available for upload/download. Optionally one can carry multiple Internet dongles from different vendors.
Portable Power Bank: This is more useful for portable devices. Carry one with a large capacity, enough for multiple recharges or charging multiple devices.
Display adapters: Necessary to troubleshoot when the main display isn’t working or to heck the display ports. Carry all combinations HDMI to VGA, MiniDisplay to VGA, MiniDisplay to HDMI, HDMI to HDMI and any others depending on the device to be connected to.
http://www.apple.com/shop/product/H9139VC/B/kanex-atv-pro-x-hdmi-to-vga-adapter-with-audio-support
http://www.apple.com/shop/product/MB572Z/B/mini-displayport-to-vga-adapter
Secondary Display: This might not be practical as displays tend to be very large and not necessarily portable. However, one can carry a small pocket projector. A secondary display is always handy as it reduces dependency on the user/client to provide one.
Power adapters: Not strictly required but can come in handy. Useful for checking if the user’s power cord is functioning properly. Make sure you carry all the different versions of the power cords.
Lightning & 30 pin cables: Again not strictly necessary but would be useful for checking if the user’s power cord is functioning properly. Make sure you carry all the different versions of the power cords.
MacBook Pro &/or iPad: Carrying your own Mac & iPhone/iPad is very important. Load these devices with various tools required to diagnose and/or fix issues.
https://itunes.apple.com/in/app/inettools-network-diagnose/id561659975?mt=8
https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/inet-network-scanner/id340793353?mt=8
Airport Utility: https://support.apple.com/kb/DL1664
Airport Utility: AirPort Utility by Apple
Continuing on from the previous post, where we learnt to secure our iOS devices, we will now apply similar steps on the Mac.
The security of a computer is easy to maintain if physical access to the device is restricted to yourself as far as possible. If any unauthorised person has physical access to your computer then all bets on security are off. While it’s easy for us to say that no one else is going to use the computer, one must always take some precautions. The following are just some of the steps one could take to secure their Mac.
This is the simplest way of ensuring very basic security. If more than one person is using a Mac one can have different accounts for each user. The account type that can be used for other users are:
This is the simplest form of security. It is the password that you use to login to the computer. Having a strong password goes a long way in securing your Mac.
A password to your account will very likely be set when it was first created.
This can be changed at any point in time.
The other approach towards changing the password is:
Note: for both the approaches you must know your existing password.
To create a strong password use the built in Password Assistant
This offers a convenient approach towards storing your files securely. Disk Images are created using Disk Utility. To create encrypted disk images:
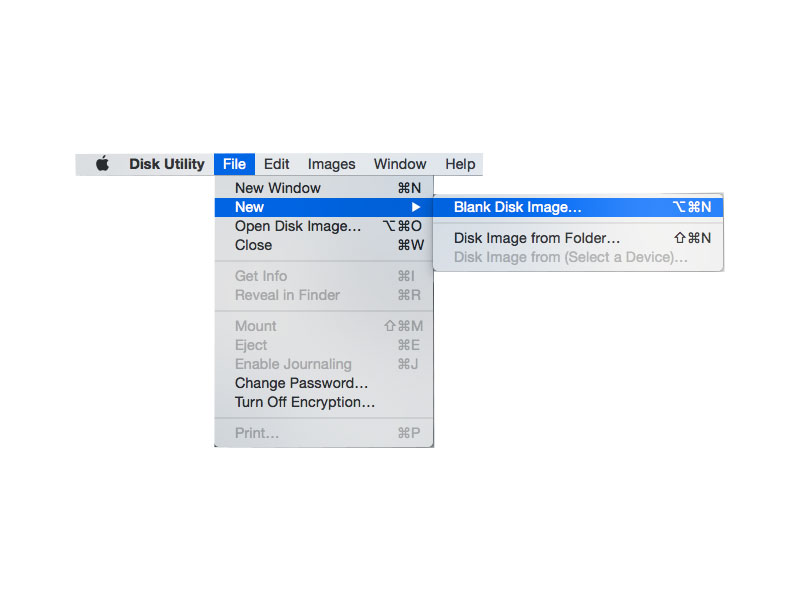
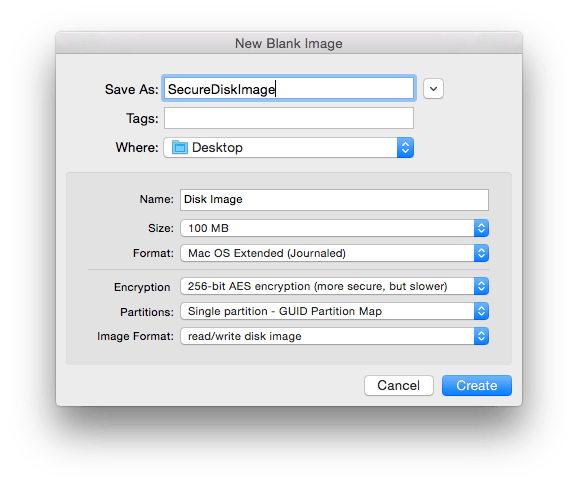
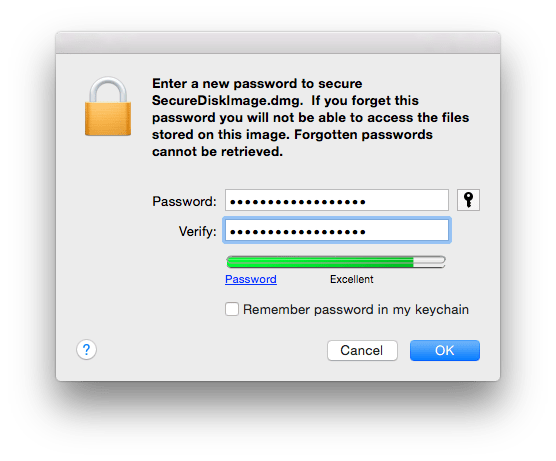
This ensures that your information is completely safe.
 The firewall option is nice if you want to secure your communications over the network. From here you can control which applications can communicate over the internet or receive communications over the network. Simply turn on the Firewall & control access to the computer.
The firewall option is nice if you want to secure your communications over the network. From here you can control which applications can communicate over the internet or receive communications over the network. Simply turn on the Firewall & control access to the computer.
To customise the access to a network:

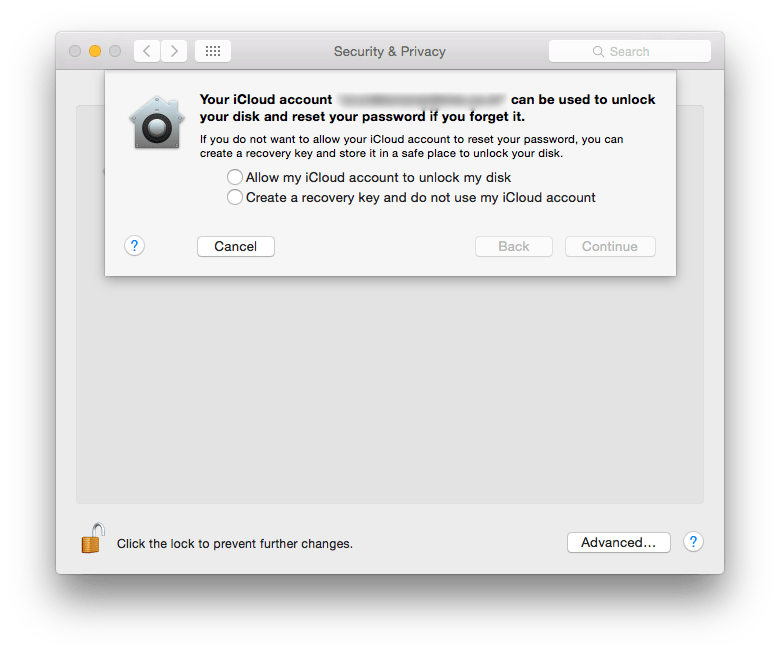
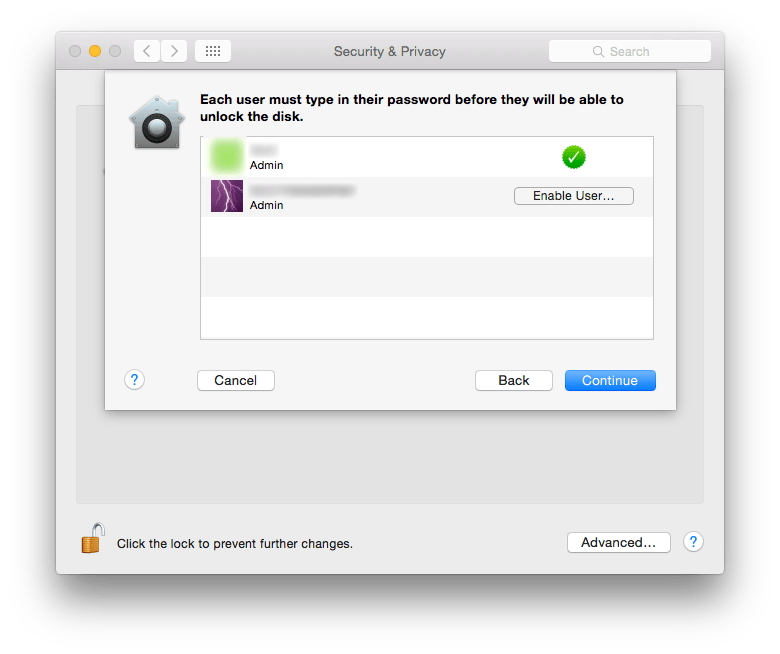
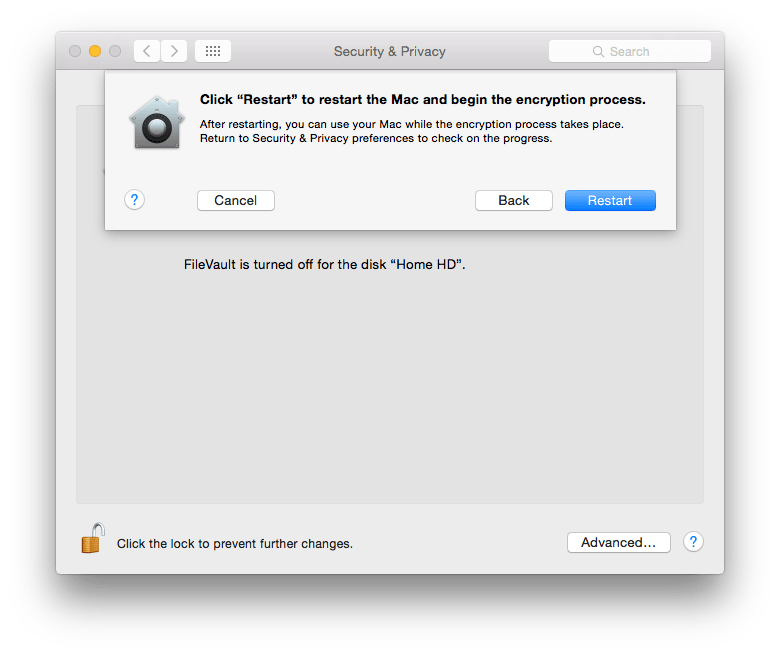
Disk images provide the option of securing some of your files. But what if there is a lot of secure information that you have? Disk images maybe used but it can become tedious if there are too many files. In such situations using FileVault to secure your files is preferable.
FileVault encrypts your main partition, that is, the partition from where you boot your OS from. Most users would have a single partition on their disk, for them it would mean that FileVault encrypts the whole hard disk. So anything you create on the encrypted partition is automatically secured.
To turn on FileVault:

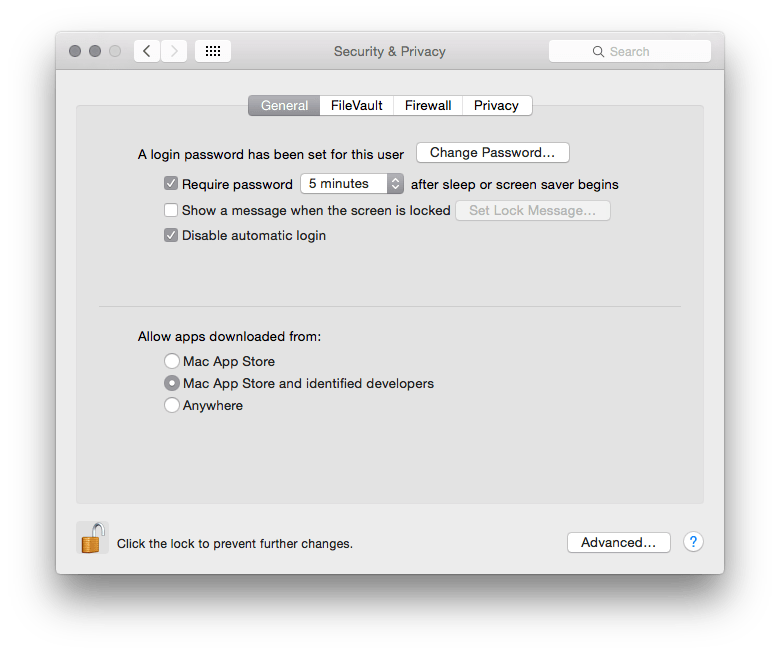
If you are leaving the computer idle or unattended for a period of time, then it is a good idea to make sure that the computer itself is locked automatically. These settings can easily be set from System Preferences:
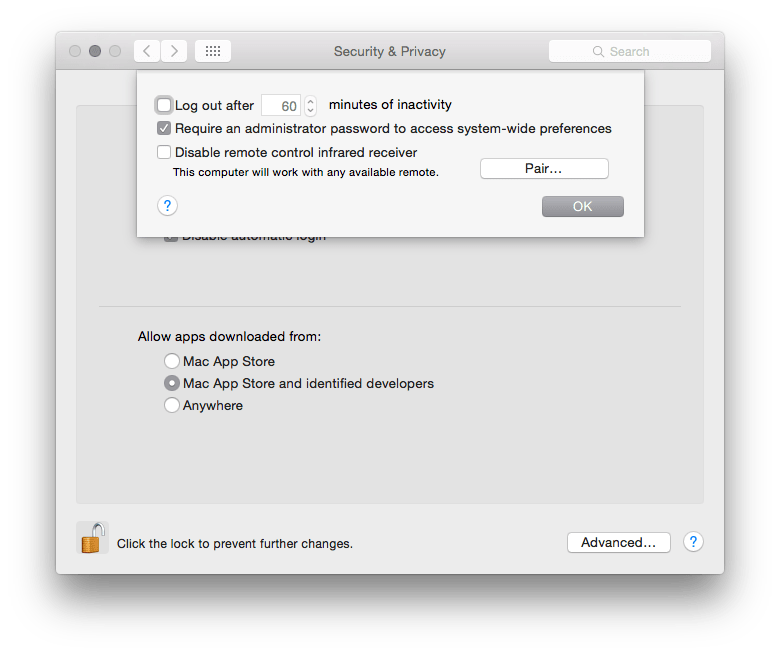
This feature has more to do with locating a device that is missing. While it is called Find My Mac, one can locate both OS X as well as iOS devices. There are a few things to keep in mind:
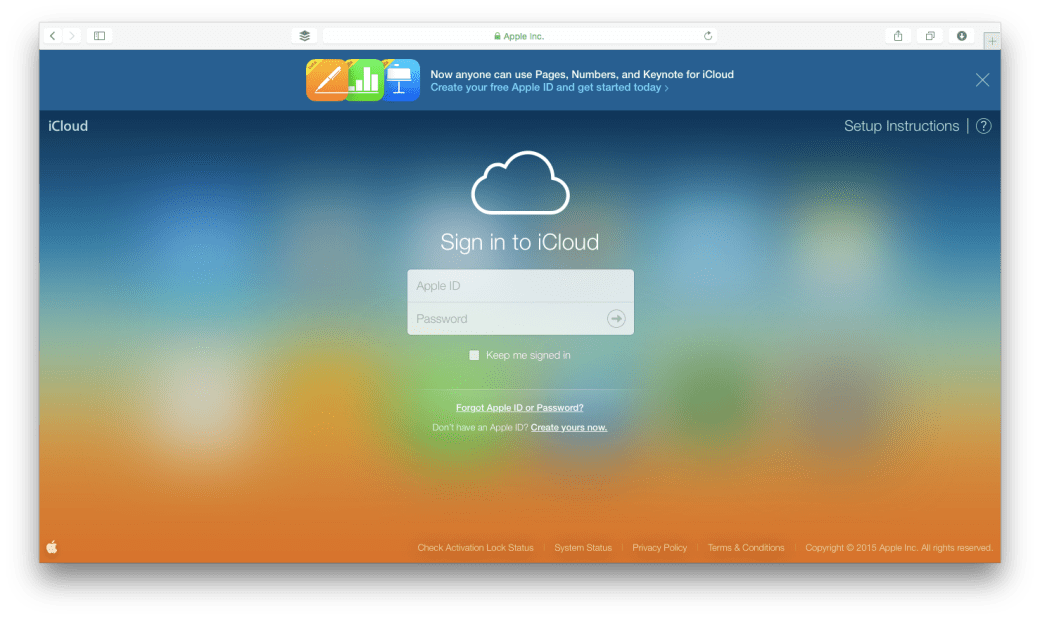
Setting up Find My Mac is easy:
Locating a device using Find My Mac:

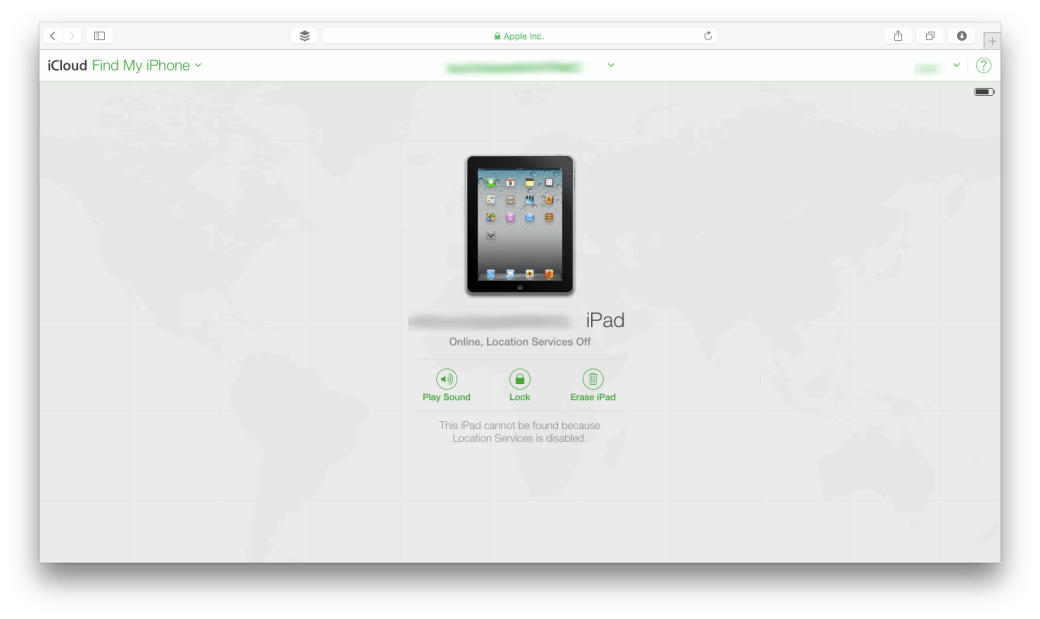
it is possible to restrict access to a particular set of data on your Mac. Through the privacy tab within System Preferences > Security & Privacy.
From here once can give access to your data at an application level. The kind of data that can be moderated are:
Certain resources such as Location & Diagnostics are controlled by the administrator.
A Firmware Password is a Logic Board level password. The main purpose of a Firmware Password is to prevent unauthorised modification of the startup process of a Mac. It doesn’t secure your data. But it makes sure that no one can gain access to your computer by changing the boot sequence. It becomes difficult for people to boot your Mac off a network or an external disk.
The process of setting up a Firmware Password is a bit technical. Please consult with a member from the IT Department of your company or contact an Apple Certified Support Professional. You can also approach an Apple Authorised Service Centre for the same. If you have forgotten one, then you will have to approach an Apple Authorised Service Centre for the same. Here are the steps.